Dna Ligase Reaction Mechanism | Ligase then transfers the amp to the 5′ phosphate end of nicked duplex dna and finally catalyzes nick closure and the release of amp. This is the currently selected item. When you ligate two strands of dna you build up a phosphodiester bond. This page has a few illustrations on this process. The reaction mechanism can be divided into three distinct catalytic.
Dna ligases share a common mechanism and a high degree of structural similarity with other members of the nucleotidyltransferase superfamily all dna ligation reactions entail sequential nucleotidyltransfer steps 18. This reaction usually involves the hydrolysis of a minor group branching off from one of the smaller molecules and usually needs atpase. The reaction mechanism involves 3 sequential nucleotidyl transfer reactions. After ligation, the insert dna is physically attached to the backbone and the complete plasmid can be. Dna repair mechanisms are, therefore, important to ensure genomic stability.

Each interacts with a partner protein during its reaction in ber. Reaction mechanism of bacterial dna ligase; This article explains the basics of dna ligation. The second step is the enzymatic reaction, which is shown schematically in figure 2. Dna ligases share a common mechanism and a high degree of structural similarity with other members of the nucleotidyltransferase superfamily all dna ligation reactions entail sequential nucleotidyltransfer steps 18. Dna replication mechanisms depend on prior events: Dna, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the biological molecule which contains the information needed to then a different enzyme, dna ligase, connects the okazaki fragments together to form the new 3' polymerase chain reaction. Pcr is a technique developed in the 1980s to amplify a specific part of. How dna is amplified using the polymerase chain reaction (pcr). Dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. Dna ligase, whose reaction is reversible, is able to relax supercoiled circular dna in the presence of amp but not in its absence. Overall, only one strand of the dna is broken during the reaction mechanism and there is no requirement of atp during the reaction. The first step is the reversible adenylation of ligase with nad+ as the adenylyl donor.
Restriction enzymes & dna ligase. This video describes the mechanism of action of dna ligase during dna replication process both in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Ligase then transfers the amp to the 5′ phosphate end of nicked duplex dna and finally catalyzes nick closure and the release of amp. This reaction usually involves the hydrolysis of a minor group branching off from one of the smaller molecules and usually needs atpase. Dna ligases are the enzymes that catalyze phosphodiester bond formation.
Outline the chemical mechanism of the ligase reaction. This reaction, called ligation, is performed by the t4 dna ligase enzyme. Structure, reaction mechanism, and function. Dna ligases are the enzymes that catalyze phosphodiester bond formation. Restriction enzymes & dna ligase. Dna repair mechanisms are, therefore, important to ensure genomic stability. Ligase then transfers the amp to the 5′ phosphate end of nicked duplex dna and finally catalyzes nick closure and the release of amp. Each interacts with a partner protein during its reaction in ber. Dna ligase joins (ligates) the free ends of okazaki fragments, resulting in a continuous strand of dna. The first step is the reversible adenylation of ligase with nad+ as the adenylyl donor. Dna ligases catalyze the repair of phosphate backbone breaks in dna, acting with highest activity on breaks in one strand of duplex dna. Overall, only one strand of the dna is broken during the reaction mechanism and there is no requirement of atp during the reaction. Ligases enzymes that attach things together.
Overall, only one strand of the dna is broken during the reaction mechanism and there is no requirement of atp during the reaction. Each interacts with a partner protein during its reaction in ber. The reaction mechanism involves 3 sequential nucleotidyl transfer reactions. Dna ligase, whose reaction is reversible, is able to relax supercoiled circular dna in the presence of amp but not in its absence. Sticky ends and blunt ends.
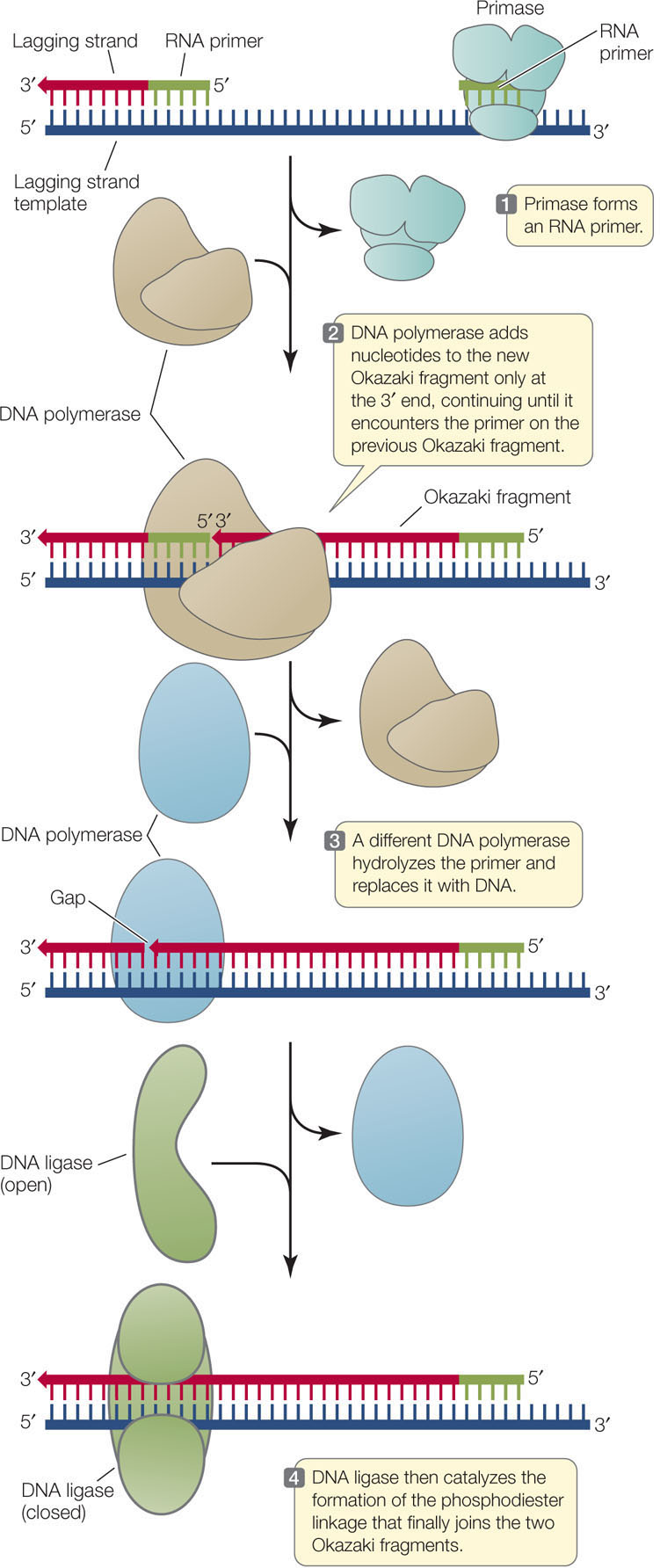
The discussion of the reaction mechanism of dna ligases in the context of the structural information for bacterial, viral, and human dna ligases and the description of protein partners of the dna ligases and how the. Dna ligases catalyze the repair of phosphate backbone breaks in dna, acting with highest activity on breaks in one strand of duplex dna. The first step is the reversible adenylation of ligase with nad+ as the adenylyl donor. To do so, you need energy, and this energy for the dna ligase comes from the then the amp is involved in the reaction itself and released afterwards. The second step is the enzymatic reaction, which is shown schematically in figure 2. The unique mechanism of dna replication at the telomeres. In molecular biology, dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. Dna, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the biological molecule which contains the information needed to then a different enzyme, dna ligase, connects the okazaki fragments together to form the new 3' polymerase chain reaction. This reaction usually involves the hydrolysis of a minor group branching off from one of the smaller molecules and usually needs atpase. Ligases enzymes that attach things together. Dna ligases are the enzymes that catalyze phosphodiester bond formation. This video describes the mechanism of action of dna ligase during dna replication process both in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The reaction mechanism involves 3 sequential nucleotidyl transfer reactions.
Overall, only one strand of the dna is broken during the reaction mechanism and there is no requirement of atp during the reaction dna ligase mechanism. This video describes the mechanism of action of dna ligase during dna replication process both in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Dna Ligase Reaction Mechanism: Dna replication requires the activity of dna polymerase, as well as other enzymes such as primase and ligase.

